The Complete 2024 Guide to Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP).

When it comes to your website, loading speed is crucial—especially with Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP).
Pages that load faster not only rank higher on search engines but also experience lower bounce rates, ensuring a more satisfying experience for your site visitors. Recognizing the significance of speed, Google has introduced various initiatives to enhance it, and one such program is Accelerated Mobile Pages, commonly known as AMP.
AMP was initially a breakthrough, prompting numerous prominent websites, like Twitter, to adopt it, with Google emphasizing its enduring relevance, especially through Accelerated Mobile Pages.
However, over the recent years, Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP) has seen a decline in discussions. Notably, Google discreetly removed the AMP symbol from search results, raising questions about its ongoing relevance.
So, what’s the story with Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP)? Is it still significant, and why did it matter in the first place?
This comprehensive guide to Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP) covers all the essentials, providing insights into what Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP) is, its significance, functionality, pros and cons, and whether it’s worth implementing for your website.
Defining Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMPs)
Accelerated Mobile Pages or AMPs like Google’s secret weapon for making websites load lightning-fast on mobiles.
Picture this: AMP trims down web pages to the bare necessities and saves a snappy version on Google servers. So, when you click, bam! Instant content delivery.
They ditch all the fancy stuff like videos, ads, and animations, focusing only on the must-haves—crucial content and images. It’s a game-changer for mobile users, letting them breeze through articles and blog posts in seconds, with no more waiting for heavy elements to load.
What Is AMP’s Aim?
AMP aims to enhance user experience by swiftly delivering content, often in a matter of seconds. Google has long prioritized the speed of webpage loading, considering it a crucial factor in ranking.
The primary objective of AMP was to boost page speed, but it seems that Google may have been motivated to rival Facebook’s instant articles and Apple News in the process.
How Did AMP Get Developed?
In 2015, the “Accelerated Mobile Pages Project” kicked off with the collaboration of notable companies like Google, WordPress, and Adobe.
This initiative drew in international news portals from the get-go, and pioneers in adopting AMP included The Guardian (UK), The Washington Post, Buzzfeed (US), Frankfurter Allgemeine Zeitung, Die Zeit (Germany), and El Pais (Spain). Twitter and LinkedIn joined as technology partners right from the start.
Fast forward to today, and almost all major online media outlets leverage AMP technology, recognizing its significant benefits in delivering speedy mobile websites.
Even WordPress users can tap into this by using appropriate plugins, although there is currently no eCommerce solution for AMP.
Technical AMP: Source Code, HTML Changes & More
Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP) is a web component framework introduced to enhance the performance of mobile web pages.
At its core, accelerated mobile pages aim to accelerate the loading speed of web content on mobile devices by streamlining the HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. The source code of an AMP page adheres to specific guidelines, favoring a simplified and efficient structure. Key components include AMP HTML, which is a restricted version of HTML with specific AMP tags and extensions, ensuring faster rendering.
CSS is streamlined through the use of inline styles and a limited set of stylesheets, optimizing the visual presentation without sacrificing speed.
JavaScript is managed through the AMP library, which prioritizes asynchronous loading and imposes restrictions on third-party scripts to prevent performance bottlenecks.
Furthermore, AMP enforces the use of a Content Delivery Network (CDN) for caching and efficient distribution of content, reducing latency for users across the globe.
AMP prioritizes mobile user experience by enforcing a comprehensive validation process, ensuring compliance with its specifications.
Although it originally gained traction in the realm of news and media, AMP has expanded its reach, covering diverse web applications.
By addressing technical intricacies and prioritizing performance, AMP plays a crucial role in shaping a more responsive and user-friendly mobile web environment.
AMP Source Code
1. General Server Compatibility with AMP Source Code:
In broad terms, any server is capable of interpreting the AMP Source Code due to its reliance on widely recognized scripts. This compatibility ensures that the code is accessible across various server environments.

2. Characteristics of AMP HTML:
AMP HTML is designed with simplicity in mind, limiting the HTML code to essential components. This results in only one HTTP request being sent when the Accelerated Mobile Page is loaded.

3. Features of AMP JavaScript:
AMP utilizes asynchronous JavaScript code, allowing the page to initiate building before all JavaScript elements have completed loading.

4. Advantages of AMP CDN:
The AMP CDN ensures global caching of every AMP website, enabling content delivery through the shortest path via a Content Delivery Network. Additionally, the CDN continuously checks the functionality of the page to prevent errors.

HTML Changes You Have To Make To Implement AMP
To ensure a website is compatible with AMP (Accelerated Mobile Pages), certain specific features must be present in its HTML. Various audiovisual elements need to be identified with specialized AMP tags such as amp-img, amp-video, amp-audio, or amp-iframe.
For instance, the inclusion of an image in the page’s source code using AMP can be demonstrated as follows:
<amp-img src=”myimage.jpg” alt=”description of the image” height=”200″ width=”300″></amp-img>
Moreover, each page must incorporate the following key elements to guarantee proper display through AMP:
- Document type: `<!doctype html>`
- Top-level tag: `<html>` tag or `<html amp>`
- Head and body tags: `<head>` and `<body>` tags
- Canonical Tag in Header: `<link rel=”canonical” href=”http://www.mynormalURL.com” />`
- Encoding: `<meta charset=”utf-8″>` within the header
- Viewport: `<meta name=”viewport” content=”width=device-width, minimum-scale=1″>`
- Reference to AMP CDN: `<script async src=”https://cdn.ampproject.org/v0.js”></script>`
- Opacity Note: <style>body {opacity: 0}</style>
<noscript><style>body {opacity: 1}</style></noscript>
Incorporating these elements ensures that the website is configured properly for optimal performance with AMP.
Pros & Cons of Accelerated Mobile Pages
AMP, or Accelerated Mobile Pages, can enhance your webpage’s speed and user interaction, but it does come with its own set of drawbacks.
Let’s dive into the positives and negatives of AMP pages:
Pros of AMP:
1. Page loading is nearly instantaneous.
2. Building pages is a straightforward process.
3. Enhances user experience on mobile devices.
4. Permits customization of designs.
5. Supported on various platforms, including Google and Bing.
Cons of AMP:
1. The AMP badge icon, once used by Google to signify AMP content, is no longer displayed.
2. Design options are limited, restricting creative elements.
3. AMP pages allow only one advertisement tag per page.
When AMP made its debut, it appeared to be a brilliant concept: Simplifying coding complexity resulted in the rapid loading of content on mobile devices. This is particularly vital given that over 50% of internet traffic originates from mobile devices.
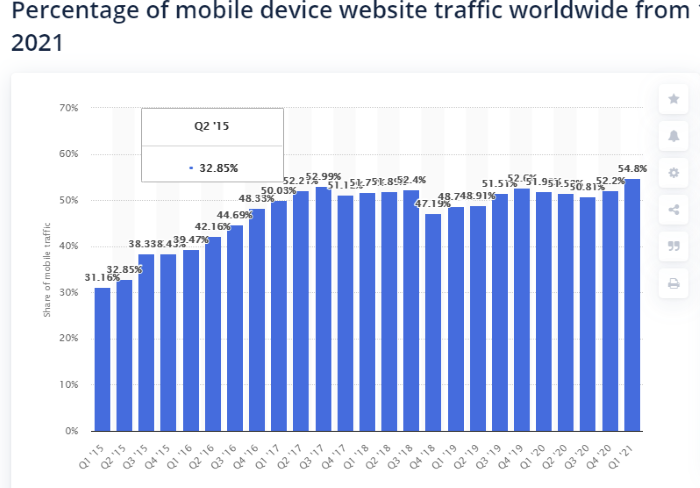
(source: Statista)
AMP tends to lean more towards the negative side when weighed against its benefits in many situations. Although the primary aim of AMP is to enhance web speed, there are various alternative methods to boost site speed that may prove more effective.
Are Accelerated Mobile Pages For You?
Many businesses often wonder whether investing time and resources in implementing Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP) is a worthwhile endeavor.
The reality is, that the answer varies depending on specific circumstances. AMP might not be the most beneficial choice for the majority of websites, especially given that Google has eliminated the AMP symbol from search results.
So, how can you determine if AMP is the right fit for your website? Consider the following factors:
- Page Speed Struggles: If your website faces challenges with page speed, despite your efforts to optimize it, AMP may be a viable solution.
- Mobile Traffic Dominance: If a significant portion of your website traffic comes from mobile devices, AMP could enhance the mobile user experience.
- Timely News Content: If a substantial amount of your content is time-sensitive news that you want to feature in Top Stories (although Google has relaxed the AMP requirement for this), AMP might still offer advantages.
However, it’s essential to note that if your website is strongly branded, serves to qualify leads, or already boasts a rapid page speed, the implementation of AMP is likely not warranted.
Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP) Best Practices for Business Owners
Are you still thinking about incorporating AMP into your website? It’s worth considering in certain situations. Before diving in, here are some key guidelines to follow:
- Assess its suitability for your website: AMP’s effectiveness has evolved, so it’s essential to determine if it aligns with your site’s needs. Check out the section on who benefits most from AMP.
- Seek assistance if you’re not using WordPress: While the AMP WordPress plug-in is user-friendly, implementing it independently can be complex. Consider reaching out to a web developer for guidance or hiring their services.
- Avoid applying AMP to high-traffic or critical conversion pages: Keep in mind that AMP removes elements such as opt-in forms and branding. Therefore, refrain from using it on pages crucial for building your brand or generating leads.
- Conduct A/B testing to gauge AMP’s impact: Leverage AMP’s support for A/B and multivariate testing to analyze its effects on metrics like conversion rate and time on page. This will help you determine if implementing AMP is worthwhile for your specific case.
What Is AMP Cache?
The Google AMP Cache serves as a reliable system for delivering cached AMP HTML pages. It operates as a proxy-based content delivery network, ensuring the efficient delivery of valid AMP documents.
By fetching, caching, and automatically enhancing the performance of AMP HTML pages, the AMP Cache plays a crucial role.
For optimal functionality, the AMP Cache ensures that it loads the document, JS files, and all images from the same origin utilizing HTTP 2.0. This approach is essential for maintaining maximum efficiency in the delivery process.
A noteworthy feature of the AMP Cache is its built-in validation system, which verifies that a page is guaranteed to function properly without dependencies on external factors that could potentially slow down the page. This validation system relies on a set of assertions to confirm that the page’s markup adheres to the AMP HTML specifications.
Furthermore, each AMP page is accompanied by an additional version of the validation system. This version is capable of logging validation errors directly into the browser’s console during page rendering. This functionality provides insights into intricate changes in code that may impact performance and user experience.
The collaborative efforts of the three core components of AMP ensure swift page loading. The upcoming section will delve into seven optimization techniques that synergize to contribute to the remarkable speed of AMP pages.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How does AMP function?
AMP streamlines pages by stripping away non-essential elements like ads, charts, videos, and animations. It then saves a version of the page on Google’s servers. When a user clicks on an AMP link, Google quickly delivers the cached content.
How can I implement AMP on my website?
For WordPress users, simply use the AMP plug-in. If you’re not on WordPress, follow Google’s provided walkthrough. If coding isn’t your forte, consider seeking assistance from a web developer.
Are AMP pages still relevant?
While not as impactful as before, AMP’s popularity has waned. Major sites are shifting away from it, and Google removed the AMP symbol from search results. Unless your site heavily focuses on timely news, the investment might not be worthwhile.
What challenges come with accelerated mobile pages?
There are several issues to consider. AMP may lead to decreased ad revenue and traffic, and obtaining analytics data about site visitors can become more challenging. Some argue it grants Google excessive control over the Search Engine Results Pages (SERPs).
Do AMP pages positively affect SEO?
AMP isn’t a must for SEO. Achieving optimal page speed and mobile experience can be accomplished through various methods. While AMP can be beneficial in specific scenarios, it shouldn’t be viewed as a definitive SEO best practice.
Conclusion
Initially, a lot of marketers jumped on the AMP bandwagon, but it’s becoming evident that the drawbacks of AMP outweigh the benefits for many websites.
With AMP no longer mandatory for Top Stories and the disappearance of the AMP symbol from search results, it’s not likely to boost your site traffic significantly.
Instead of fixating on AMP, prioritize enhancing your site speed and ensuring a user-friendly experience on mobile devices. That’s the optimal approach to draw in mobile customers and foster business growth.
People Also Read:
Rank higher with these 5 Mobile SEO Tips.
9 Actionable Tips For SEO Beginners.
How Does Link-Building Strategy Work For SEO?




